Settlement is where the rubber meets the road in online payments. This is when the money your customers parted with moves from their bank to yours. Understanding this process isn’t just for finance professionals; it’s crucial for anyone running a business that accepts online payments. From small startups to corporate giants, a clear grasp of settlements can mean the difference between a healthy cash flow and a financial headache.
So, what exactly happens during a settlement? What factors influence settlement times? How do you reconcile your payments? And what does the future hold for this often-overlooked aspect of online business? We’re about to explore these questions and more.
Whether you’re considering a new payment processor or fine-tuning your existing setup, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
What is payment settlement
Payment settlement occurs when the acquiring bank – your business’s banking partner – collects the cash from the customer’s issuing bank (their bank) through the payment gateway.
Who’s who in every transaction?
To fully grasp the payment settlement process, let’s introduce the key players:
- The merchant: You, the business selling goods or services.
- The customer: The person buying from you.
- The acquiring bank: Your bank that processes card payments.
- The issuing bank: The customer’s bank.
- The payment processor: The tech company managing the transaction flow.
- Card networks: The Visa, Mastercard, etc., that set the rules.
- Payment gateway: The software that connects your website to the payment processor.
- Central banks and regulatory bodies: They oversee the entire system.
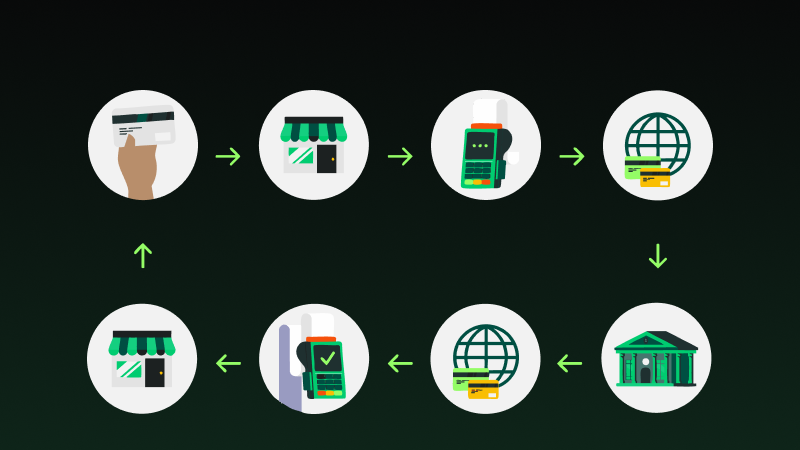
How does payment settlement work?
Online payments involve a complex process of transferring funds between the customer, merchant, and financial institutions. Here’s how the settlement process works.
Customer initiates payment
The online payment process begins when a customer selects a product or service and proceeds to checkout. They input payment details, such as credit card information or digital wallet credentials. After payment verifications, the customer authorizes the transaction.
Authorization request and approval
Upon receiving the payment request, the merchant’s payment gateway sends an authorization request to the customer’s issuing bank. The inquiry checks if the customer has enough money or credit to pay for the transaction. If approved, the issuing bank authorizes the transaction and sends a response to the payment gateway.
Capture and settlement
After the issuing bank grants the authorization, the merchant typically reserves the authorized funds through the capture process. Capture holds the funds in a pending state until the order is fulfilled or shipped. Once the merchant completes the order, they start the payment settlement process, which transfers the authorized funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
Funds transfer to merchant account
The settlement process involves multiple parties, including the payment gateway, acquiring bank (the merchant’s bank), issuing bank, and card networks.
- The acquiring bank collects the funds from various merchants and transfers them to the card networks.
- Card networks then distribute the funds to the issuing banks, which credit the customer’s account.
- The merchant receives the funds in their account, minus any processing fees.
Gross vs. net settlement: Which is right for you?
You have two choices for how your payment service provider can manage your earnings: gross or net settlement.
With gross settlement, every transaction is a standalone action. The money from each sale hits your account instantly, without deductions. However, you’ll need to pay transaction fees later.
Net settlement is different. Your PSP bundles your daily transactions. You receive a single payment at a designated time after fee deductions.
So, which one is better? Well, that depends. Gross settlement is great for high-value or time-sensitive transactions. You want that money in your account ASAP and are okay with dealing with fees later. Net settlement is ideal for businesses that prefer a clear-cut daily figure and don’t mind waiting a bit for their money.
Ultimately, your best choice depends on your business needs and risk tolerance.
Fraud prevention in settlements
The payment settlement process is where digital promises turn into cold, hard cash. Yet, a silent menace looms in the darkness: fraud. It’s not a matter of if you’ll face it, but when.
Common payment fraud types
A comprehensive understanding of fraud schemes is essential for effective prevention. Commonly encountered payment fraud types include:
- Chargebacks: The reversal of a transaction started by the cardholder, often resulting in financial loss for the merchant.
- Friendly fraud: A specific type of chargeback where the cardholder denies authorizing a legitimate purchase.
- Account takeover (ATO): Unauthorized access to a customer’s account for fraudulent transactions.
- Triangle fraud: A complex scheme involving collusion between a merchant, cardholder, and fraudster to deceive the payment processor.
But you’re not defenseless. Payment processors and banks are on the front lines, throwing up a wall of protection around your business.
Security measures implemented by payment processors and banks
Payment service providers and financial institutions invest significantly in security infrastructure to protect transactions. Common safeguards include:
- Tokenization: Substituting sensitive card data with non-sensitive tokens to reduce data exposure.
- Encryption: Safeguarding data transmission through encryption protocols. Data encryption ensures your payment details are safe during transmission and storage.
- Fraud detection systems: Employing advanced analytics to identify suspicious transaction patterns. As Effectiv reports, many banks and financial institutions have invested in AI systems to improve their fraud detection.
- Biometric authentication: Leveraging biometric data like fingerprints and face detection for enhanced security.
- Chargeback management Tools: Providing merchants with resources to dispute fraudulent chargebacks.
Understanding threats, leveraging available tools, and implementing robust security measures reduce your exposure to fraud. Remember, prevention is always better than a cure.
Payment settlement best practices
Online payments fuel modern businesses. A stable settlement strategy is vital to optimize this process and reduce risks.
Clearly define roles and responsibilities within your team to streamline payment processing. Establish precise payment terms in contracts, including due dates and penalties for late payments, to prevent bottlenecks and disputes.
Prioritize security by partnering with reputable payment platforms that adhere to industry standards like PCI DSS. Regularly update systems and employ strong encryption to safeguard customer data. Strict adherence to data protection laws and robust access controls protect against breaches.
Reconcile payment records against bank statements and internal books regularly. Constant evaluation helps uncover discrepancies and potential fraud. Monitor transactions closely for anomalies and conduct audits to identify process weaknesses.
Stay updated on payment laws and regulations to ensure compliance. Implement rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures to verify customer identities and protect your business from fraud. Keep your team informed about the latest payment security best practices and regulatory changes.
Finally, develop a process for handling chargebacks and disputes efficiently. Document every step to protect your business.
Choosing the right payments partner
Selecting the ideal Payment Service Provider (PSP) is crucial for online businesses. To make an informed decision, you must first understand your business.
- Consider your business size, industry, growth trajectory, and target customer base. A PSP that aligns with these characteristics will efficiently support your operations.
- Understanding your customers’ payment preferences is essential for optimizing the checkout experience and boosting conversion rates. A diverse range of payment methods can enhance customer satisfaction.
Learn how your business can keep clients happy with the right payment methods in our detailed guide.
Key features to look for in a PSP
Reliability, authorization rates, and pricing transparency are fundamental when evaluating a PSP.
- A reliable provider ensures uninterrupted service, especially during peak sales periods. High authorization rates directly impact your bottom line by reducing checkout abandonment.
- Transparent pricing models with no hidden fees are essential for effective financial management. Choose a PSP with flexible pricing plans to accommodate your business growth.
Find out more about merchant fees in our comprehensive guide.
The importance of customer support and security
A responsive and knowledgeable support team is invaluable for addressing technical issues, chargebacks, and other challenges. A PSP that prioritizes excellent customer support can save you time and frustration.
Data security is important in the payments industry. To protect your customers’ sensitive information, ensure your PSP complies with industry standards like PCI DSS.
APS: Your trusted payment partner
APS is committed to providing reliable payment solutions for businesses of all sizes. Contact us today to learn more about our offerings and how we can support your payment processing needs.
FAQs
What is payment settlement?
Payment settlement is the final stage of a transaction where funds move between the buyer and seller. It occurs after the authorization process, which verifies the buyer’s ability to pay.
Payment settlement requires processing the transaction through financial networks, reconciling accounts, and transferring funds to the relevant parties. The usual timeframe for this process is a few business days, but faster settlement times are possible with specific payment methods.
What is a payment settlement system?
A payment settlement system is the digital infrastructure that handles the final transactions between the buyer and seller. When a payment is authorized and validated, the settlement system takes effect, ensuring the money reaches the right account. Think of it as the accountant making sure everyone gets paid.
Sources