Running a business is like keeping a machine humming – everything needs to work for a smooth customer experience. Yet, many online entrepreneurs overlook a crucial cog—the payment gateway.
It’s hard to select a payment partner when there’s so much information on the internet, but no clear communication on what you need to know about payment gateways.
In this article, we’ll be sharing the basics of payment gateways. Let’s dive in.
What is a payment gateway?
Payment gateways are secure platforms that enable electronic transactions between customers, businesses, and financial institutions. They simplify the acceptance, processing, and handling of various payment methods, such as credit cards, debit cards, and digital wallets.
The rise of e-commerce in the late 20th century drove the need for secure ways to make and receive payments. Early payment gateway systems, primarily manual, faced significant security concerns. Introducing SSL encryption in the late 1990s marked a turning point. Today, payment gateways offer integrated solutions prioritizing user experience and security through features like tokenization and two-factor authentication.
Payment gateways are essential for online businesses. They provide a secure transaction platform, enhancing customer experience and payment efficiency. Strong security measures and the ability to facilitate global transactions allow firms to reach a broader audience, increasing sales and revenue.
How do payment gateways work?
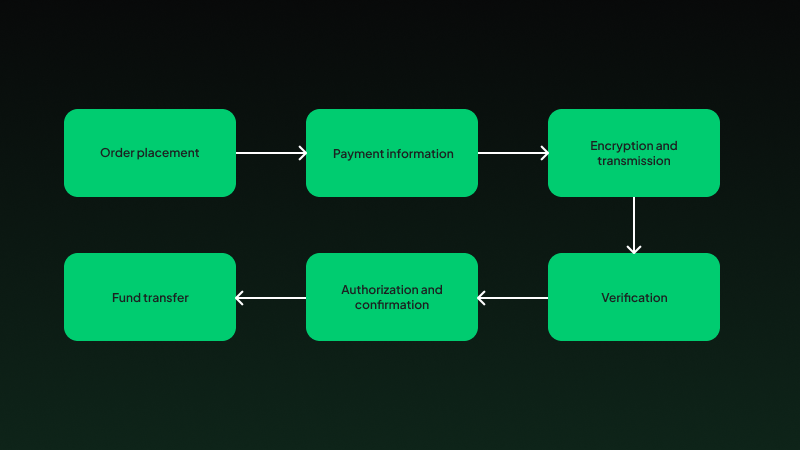
Now that we’ve defined payment gateways, let’s explore how they work. Here’s a breakdown of the transaction process:
- Order placement: The customer starts by placing an order on your website.
- Payment information: They enter payment details, such as credit card information, on a secure payment gateway interface.
- Encryption and transmission: The payment gateway encrypts the information for security and sends it to the payment processor, typically a bank or financial institution.
- Verification: The payment processor checks the information and verifies the availability of funds.
- Authorization and confirmation: The payment gateway receives authorization from the payment processor and sends a confirmation to the merchant and the customer, indicating the transaction’s approval.
- Funds transfer: The funds are transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account, usually within a few business days.
Customer data security is paramount throughout this process. The payment gateway protects the data using encryption. Secure protocols and data protection measures help payment gateways prevent fraud.
Types of payment gateways
Payment gateways are the workhorses of online transactions, but did you know there’s more than one type? Let’s break down the main options:
Merchant account gateways
Merchant account gateways require businesses to have a merchant account with a bank or payment processor. They offer robust features like recurring billing and advanced fraud prevention, making them ideal for established businesses.
Payment aggregators
Payment aggregators act as intermediaries, managing merchant accounts and processing payments for a fee. They are easier to set up and suitable for small businesses or startups, though they may have higher transaction fees.
Besides the two main options, there are 4 payment gateway types based on their technical characteristics.
Hosted payment gateway
This gateway, hosted by a third-party service provider, redirects customers to the payment provider’s page to complete transactions. Since the provider handles all payment data, it’s ideal for businesses that want security and simplicity.
API-hosted payment gateway
Enterprises integrate API-hosted payment gateways into their website or app via an API. When paying for services, clients provide their payment information directly on the site or app, providing a smooth checkout experience. API-hosted payment gateways are great for businesses wanting more control over their checkout process.
Self-hosted payment gateway
Businesses using a self-hosted gateway collect payment information on their own site and then send it to the gateway for processing. Self-hosted gateways offer greater control and customization but require strict security measures to protect client data.
Local bank integration gateway
This type redirects customers to the payment gateways page to complete the transaction and return to the business website. It’s a good fit for businesses looking to integrate with local banks for localized payment solutions.
Bonus: Digital currency payment gateways
These payment gateways enable businesses to accept digital currencies. They offer a way to tap into the growing market of digital asset users.
Features of a good payment gateway
When choosing a payment gateway, businesses should consider the following key features.
Security
A safe gateway should be PCI compliant, offer fraud prevention tools, and use data encryption to protect sensitive information. These measures ensure the safety of your business and customers from potential threats.
Payment methods supported
With payment flexibility, your business attracts a broader client base. The gateway you select needs to support a variety of payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, e-wallets, digital currencies, and recurring billing options.
Fun fact
APS facilitates secure and reliable payments across more than 200 countries, with over 30 online payment methods
Integration with a business platform
A good payment gateway should easily integrate with your website or online platform.
Transaction fees
Understand the fees involved, including:
- Processing fees
- Monthly fees
- Chargeback fees
Additionally, check that the payment gateway you select provides all its fees upfront to avoid surprises during payment and settlement.
Reporting and analytics
The gateway should offer tools to track sales and analyze customer behavior. Access to detailed reports and analytics provides valuable insights into your business performance and customer preferences.
Customer Support
Consider the availability and quality of merchant customer support. With reliable customer support, you can present your issues and have them solved quickly.
The advantages and disadvantages of payment gateways
Like all technologies, payment gateways have their set of considerations.
| Benefits of using payment gateways | Challenges of payment gateways |
|---|---|
| Increased sales: By offering customers convenient payment options, businesses can see higher conversion rates and increased sales. | Multiple fees: These fees can reduce profit margins, especially for businesses with high transaction volumes. |
| Improved security: Payment gateways handle sensitive data securely, reducing the risk of fraud. They use encryption and comply with regulations like PCI DSS. | Integration complexity: Setting up and integrating a payment gateway with your platform may require technical expertise. |
| Streamlined payment processes: These gateways simplify payment processing and reconciliation with automated features, saving time and reducing errors. | Merchant account requirements: Not all businesses qualify for a merchant account, which can limit their gateway options. |
| Global reach: Accept payments from customers worldwide, expanding your market beyond local boundaries. | Security breaches: Despite security measures, choosing a reputable provider is crucial to minimize the risk of breaches. |
Technologies shaping the future of seamless transactions
So, what are payment gateways integrating to provide better transaction services?
Frictionless checkout – One-click and biometric authentication methods make purchases quicker and more convenient. These technologies aim to create a smoother customer experience both online and in-store.
Are you curious about closing more sales at the checkout? Learn how to simplify your checkout process with APS.
Mobile wallets – These are becoming more popular, simplifying online payments. Digital wallets have gained widespread adoption, allowing users to pay with just a tap of their smartphones.
Artificial Intelligence – AI algorithms are increasingly used for fraud detection and prevention, enhancing online transaction security. Machine learning and AI in fraud prevention are key trends shaping the digital payments landscape.
These trends are transforming how businesses and consumers conduct transactions and shaping the global economy.
Blockchain technology – Blockchain has the potential to enable secure and transparent peer-to-peer transactions, changing how we conduct online payments. Digital currencies, once considered niche, are becoming increasingly mainstream, offering new avenues for financial transactions and investments.
The verdict on payment gateways
Payment gateways form the foundation of secure online businesses by simplifying transactions and earning customer trust. Explore various providers to find a solution that aligns with your business transactions. Remember, a reliable and secure payment gateway is an investment in your success.
FAQs
1. What are payment gateways?
Payment gateways are financial services that process payments for online and brick-and-mortar stores. They act as intermediaries between the merchant and the bank, ensuring secure transactions.
2. How do payment gateways work?
Payment gateways encrypt and transmit payment details from the customer to the merchant’s bank, then return authorization or decline messages. When a customer makes a purchase, the payment gateway securely sends the transaction data to the payment processor, which then communicates with the customer’s bank to authorize the payment. Once approved, the funds are transferred to the merchant’s account, completing the transaction.
3. How much do payment gateways charge?
Payment gateway fees vary depending on the provider. Merchants must understand and compare these costs, typically including setup, transaction, and monthly fees. Always ensure the provider discloses all charges upfront.
Sources